© C. Rüter · M. Bielaszewska

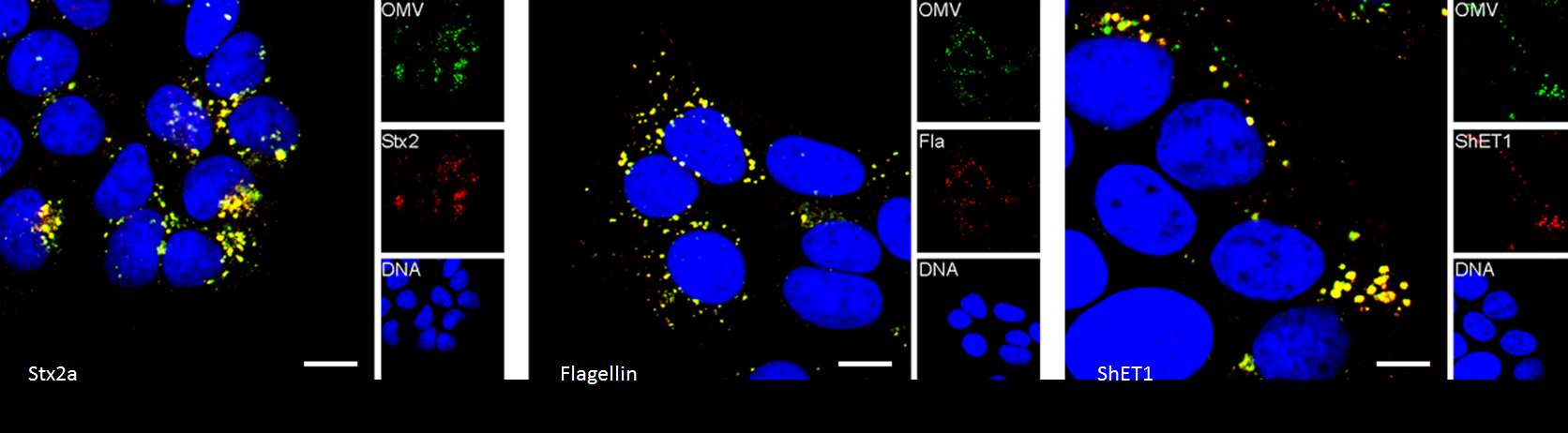
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) secrete a cocktail of exotoxins, which in concert breach the intestinal epithelial and endothelial barrier, and cause severe complications such as the hemolytic uremic syndrome. This project is aimed at unraveling the interplay of virulence factors of EHEC serotypes O157:H- and O104:H4 and the role that host factors play in this process. Understanding the interactions of the individual determinants could form the basis for developing preventive and specific therapeutic measures for EHEC infections.
Research area: Infection biology, pathogenesis
Prof. Dr. med. Alexander Mellmann
Funding period: July 2012 - June 2020
Original articles